Application Of X Ray Crystallography Slideshare
The electron surrounding the molecule diffract as the x rays hit them.
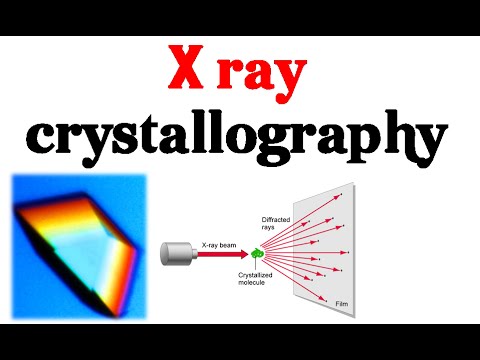
Application of x ray crystallography slideshare. Pharmaceutical scientists hoped that by blocking this enzyme they could prevent the virus from spreading in the body. This forms a pattern. X ray crystallography is a technique used to determine the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal in which the crystalline atoms cause a beam of incident slideshare uses cookies to improve functionality and performance and to provide you with relevant advertising. From the angles and intensities of these diffracted beams a crystallographer can produce.
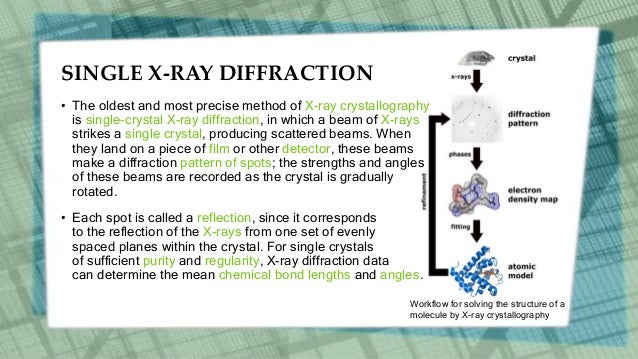
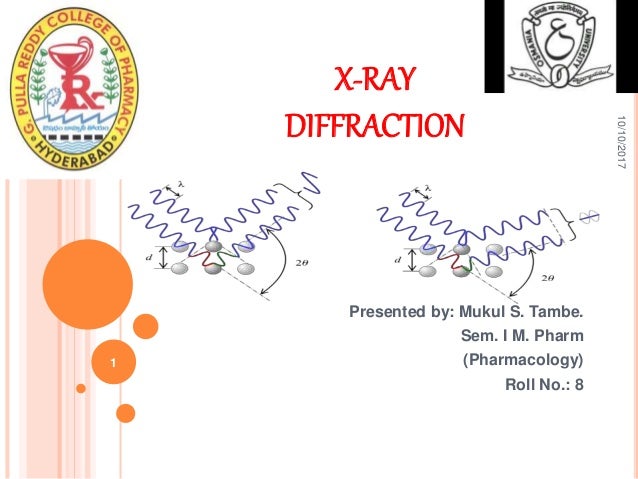
Introduction x ray crystallography is a method of determining the arrangement of atoms within a crystal in which a beam of x rays strikes a crystal and causes the beam of light to spread into many specific directions. X ray diffraction diffraction is the slight bending of light as it passes around the edge of an object. For analytical purposes range of 0 7 2 0 anstrons. X ray crystallography uses the uniformity of light diffraction of crystals to determine the structure of molecules or atoms.
X ray penetrates flash but not bone. Structures containing air will be black on film and muscle fat and fluid will. This forms a pattern. Hence use of it is a technique which relies on the dual x ray crystallography technique is useful for nature wave particle.
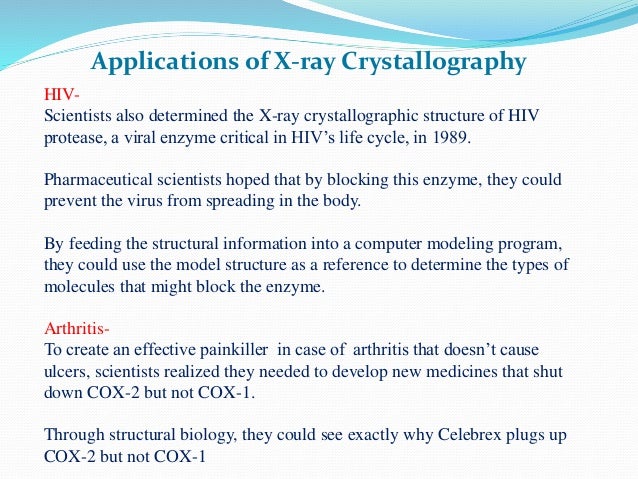
Applications of x ray crystallography hiv scientists also determined the x ray crystallographic structure of hiv protease a viral enzyme critical in hiv s life cycle in 1989. X ray crystallography uses the uniformity of light diffraction of crystals to determine the structure of molecule or atom then x ray beam is used to hit the crystallized molecule. The electron sorrounding the molecule diffract as the x rays hit them. X rays are generated when light velocity electrons are on the the metal target.
Then x ray beam is used to hit the crystallized molecule. The electrons surrounding the molecule diffract as the x rays hit them. Then they use an x ray beam to hit the crystallized molecule. For proteins appropriate size is of the x ray crystallography order of å 10 10 m.
X ray diffraction wave length of x ray region 0 1 to 100 a anstrons. Bone will block most of the photons.